- Home
- Tendinitis
Tendinitis
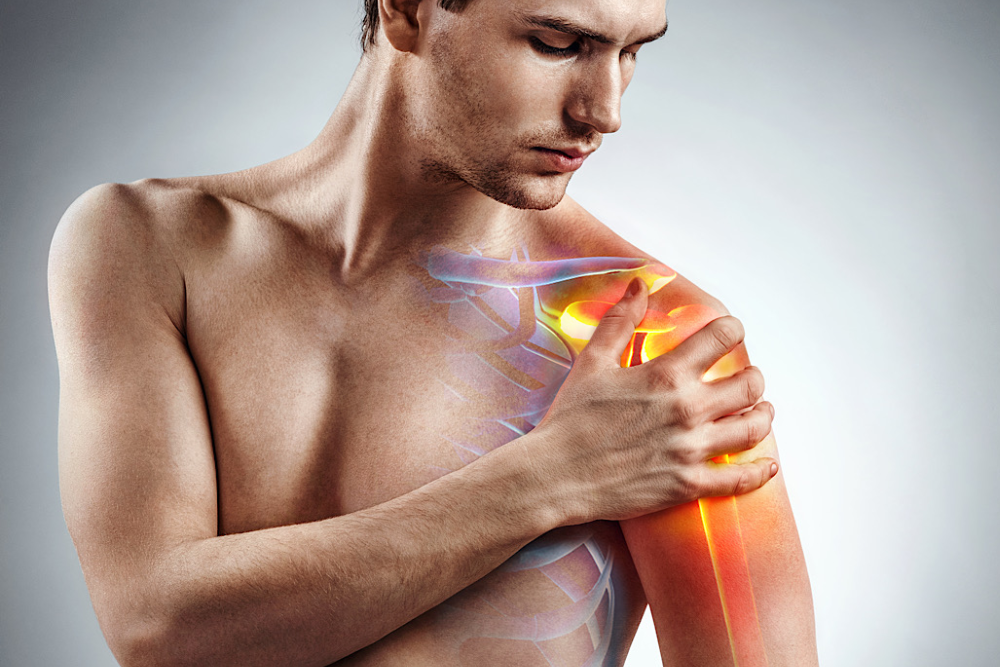
Tendinitis
di FIT Therapy Technology Academy
What is tendinitis?
Tendinitis is a medical condition characterised by inflammation of a tendon, which is a fibrous structure that connects a muscle to a part of the bone. The tendons are responsible for transmitting the force generated by the muscles to the bone, allowing the joints to move. When a tendon becomes inflamed, tendinitis occurs.
Causes of tendinitis
Common causes of tendinitis include excessive or repetitive use of a muscle or muscle group, acute or chronic injuries, or even age-related changes in the tendons. Tendinitis can affect different parts of the body, including the elbow (in the case of tennis elbow or golfer’s elbow), shoulder (in rotator cuff tendinitis), wrist, knee, hip and the Achilles tendon in the heel.
Symptoms
Typical symptoms of tendinitis include pain in the affected area, swelling, stiffness and sometimes weakness in movement. Treatment of tendinitis usually involves rest, the application of ice, stretching and strengthening exercises, physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory drugs and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections. In more severe or chronic cases, surgery may be necessary. It is important to consult a doctor if you suspect you have tendonitis, as early diagnosis and proper treatment can help prevent complications and promote a speedy recovery.
FIT Therapy Technology and treatment protocols.
The treatment of tendonitis can vary depending on the severity and location of the tendonitis, but in general, there are some common treatment protocols that can be followed. It is important to note that you should always consult a medical professional for an accurate assessment and specific treatment guidance. Here are some of the typical approaches for treating tendonitis:
- Rest: The first thing to do when tendonitis is suspected is to avoid or reduce the activity that is causing the problem. Rest is essential to allow the tendon to heal.
- Application of ice: Applying ice to the inflamed area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can design a specific exercise programme to help strengthen surrounding muscles, improve flexibility and speed up recovery.
- Physical therapies: Some physical therapies, such as ultrasound or shock wave therapy, can be used to promote healing and reduce pain.
- Orthoses: The use of braces or supports can help stabilise the affected joint and reduce the load on the tendons.
- Cold or heat therapy: The application of moist heat or cold compresses can help relieve pain and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and commit to the recommended treatment programme. Preventing tendonitis is just as important, and this can be done by avoiding excessive or repetitive use of muscles, maintaining correct posture and strengthening muscles through regular exercise.
FIT Therapy Patch Treatment Method
The FIT Therapy Patch can be used to treat painful events related to tendinitis.
It proves to be a valid natural alternative to the use of medication or devices that release heat.
Instructions for proper application (also watch the video tutorial):
- Remove the patch from the base.
- Apply the patch to dry, clean, and hair-free skin.
- Wait about two minutes for better adhesion of the patch to the skin.
- Keep the patch applied for 5 days.
- Continue the therapy until an improvement in symptoms is observed.
The patch retains its function even when wet (e.g., during a shower).










